Íomhá:Aral sea.gif
Cuma
Méid an réamhamhairc seo: 600 × 600 picteilín. Other resolutions: 240 × 240 picteilín | 480 × 480 picteilín | 720 × 720 picteilín.
Taispeáin leagan ardtaifigh den íomhá (720 × 720 picteilín, méid comhaid: 3.16 MB, cineál MIME: image/gif, looped, 12 frames, 12 s)
Stair chomhaid
Cliceáil ar dáta/am chun an comhad a radharc mar a bhí sé ag an am sin.
| Dáta/Am | Mionsamhail | Toisí | Úsáideoir | Nóta tráchta | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
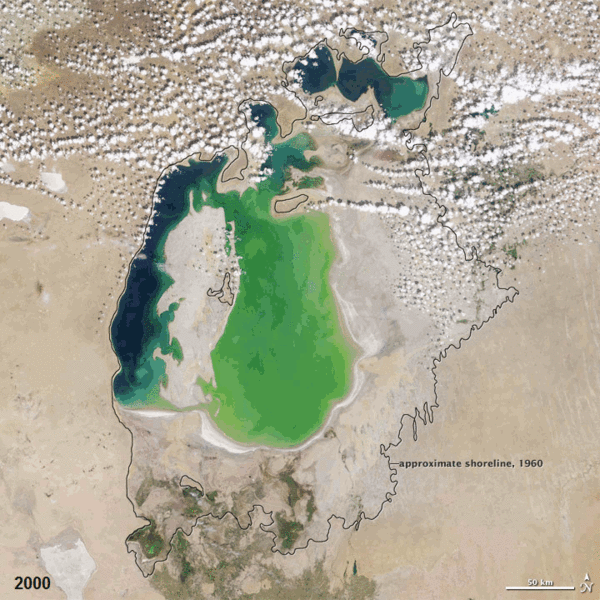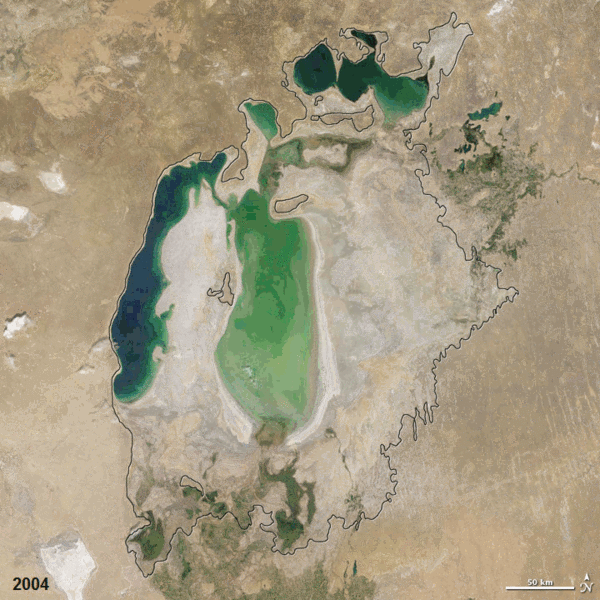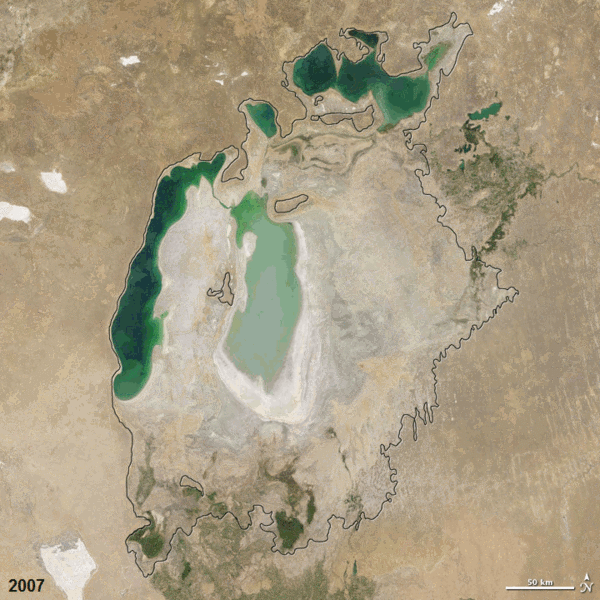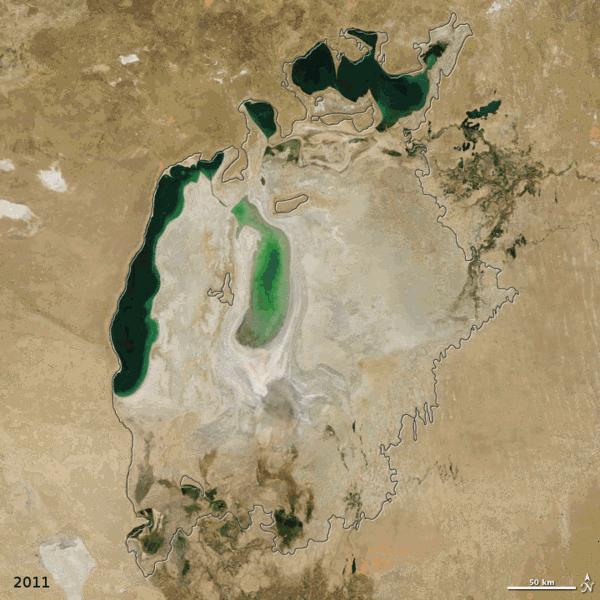
| faoi láthair | 07:38, 19 Nollaig 2011 | 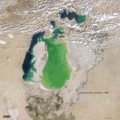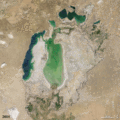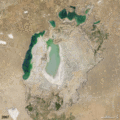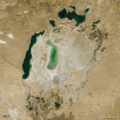 | 720 × 720 (3.16 MB) | ComputerHotline | == Summary == {{Information |Description={{en|In the 1960s, the Soviet Union undertook a major water diversion project on the arid plains of Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan. The region’s two major rivers, fed from snowmelt and precipitation in |
| 12:19, 25 Nollaig 2010 |  | 720 × 720 (2.92 MB) | ComputerHotline | == Summary == {{Information |Description={{en|In the 1960s, the Soviet Union undertook a major water diversion project on the arid plains of Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan. The region’s two major rivers, fed from snowmelt and precipitation in |
Úsáid comhaid
Tá nasc chuig an gcomhad seo ar na leathanaigh seo a leanas:
Global file usage
Úsáidtear an comhad seo ar na vicithe seo a leanas:
- Úsáid ar ba.wikipedia.org
- Úsáid ar ca.wikipedia.org
- Úsáid ar en.wikibooks.org
- Úsáid ar es.wikipedia.org
- Úsáid ar et.wikipedia.org
- Úsáid ar eu.wikipedia.org
- Úsáid ar fr.wikipedia.org
- Úsáid ar hsb.wikipedia.org
- Úsáid ar kk.wikipedia.org
- Úsáid ar pl.wikipedia.org
- Úsáid ar ro.wikipedia.org
- Úsáid ar ru.wikipedia.org
- Úsáid ar ru.wikibooks.org
- Úsáid ar ru.wikinews.org
- Úsáid ar simple.wikipedia.org
- Úsáid ar sk.wikipedia.org
- Úsáid ar uz.wikipedia.org



